Wiggle Sort I & II
如何利用单调性
怎么 partition
什么顺序穿插
如何 in-place
看起来像Partition Array又不像的两道题。Google很喜欢这两道。
280. Wiggle Sort
首先这题一看就是要你 O(n) 解的,而且要 in-place,不然毫无挑战,因为 quick sort 都 O(n log n)
这题在条件上,比 Wiggle Sort II 要宽松,因此代码变的可以很简单。
这题还有一个google面经题变种,在这个帖子中,思想非常类似,更利于思考 wiggle sort 的本质
public class Solution {
public void wiggleSort(int[] nums) {
if (nums == null || nums.length == 0) return;
boolean findBigger = true;
for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; ++i) {
if (findBigger) {
if (nums[i] < nums[i - 1]) {
swap(nums, i, i - 1);
}
} else {
if (nums[i] > nums[i - 1]) {
swap(nums, i, i - 1);
}
}
findBigger = !findBigger;
}
}
private void swap(int[] nums, int a, int b) {
int tmp = nums[a];
nums[a] = nums[b];
nums[b] = tmp;
}
}
324. Wiggle Sort II
在 Wiggle Sort I 的基础上拿掉了等于号条件,整个题都难了好多,因为这次如果相邻两个数是相等的,怎么 swap 都不符合题意。如果单纯的按顺序扫,就不可避免的会遇到到“找正确元素”的步骤,这个步骤一旦多了,复杂度就上去了。
先写个时间空间复杂度都不对的写法,只要用到了排序,时间复杂度就比O(n)大了。这是一个初步的思路。从后往前依次找剩余元素中最大的,按正序插入数组。
public class Solution {
public void wiggleSort(int[] nums) {
if (nums == null || nums.length < 2) return;
Arrays.sort(nums);
int[] result = new int[nums.length];
int index = nums.length - 1;
for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; --index) {
result[i] = nums[index];
i += 2;
}
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; --index) {
result[i] = nums[index];
i += 2;
}
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; ++i) {
nums[i] = result[i];
}
}
}
不得不说,Leetcode论坛藏龙卧虎,有个人想了个virtual indexing的方法。
A(i) = nums[(1 + 2*i) % (n | 1)]
(n|1) 强行变奇数。
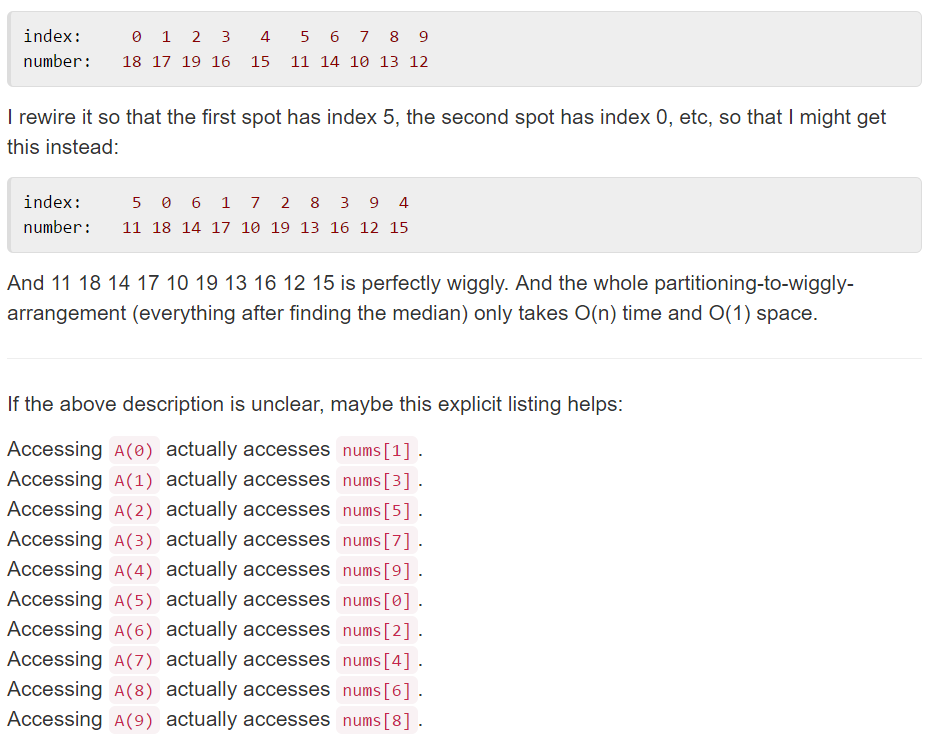
实际上是先用sort colors算法从大到小三分数组,然后找到median再进行virtual indexing。
上面那个 sort 之后从大到小正序穿插插入的顺序,和这题一样,不同之处是,这个写法更符合题目的本质:不需要排序,只需要 partitioning。 正确 partition 的数组只要按照这个顺序插入,都是正确的。median是用findKthLargest那道题的做法去找的。
于是问题就分成了三个子问题:
怎么 partitioning
什么顺序穿插
如何 in-place
public class Solution {
public void wiggleSort(int[] nums) {
int median = findKthLargest(nums, (nums.length + 1) / 2);
int n = nums.length;
int i = 0;
int left = 0;
int right = nums.length - 1;
while (i <= right) {
if (nums[newIndex(i, n)] > median) {
swap(nums, newIndex(left++, n), newIndex(i++, n));
} else if (nums[newIndex(i, n)] < median) {
swap(nums, newIndex(right--, n), newIndex(i, n));
} else i++;
}
}
private int newIndex(int index, int n) {
return (1 + 2*index) % (n | 1);
}
private void swap(int[] nums, int a, int b) {
int tmp = nums[a];
nums[a] = nums[b];
nums[b] = tmp;
}
}